|
Each year since 2002, the four New Jersey Electric Distribution Companies (EDCs) -
Public Service Electric and Gas Company (PSE&G),
Jersey Central Power & Light Company
(JCP&L),
Atlantic City Electric Company (ACE),
and Rockland Electric Company (RECO) - have procured several billion dollars of electric supply to serve their Basic Generation Service (BGS) customers through a statewide Auction Process held in February. BGS refers to the service of customers who are not served by a third party supplier or competitive retailer. This service is sometimes known as Standard Offer Service, Default Service, or Provider of Last Resort Service. Starting in 2003, the needs of residential and smaller commercial customers were met through a statewide auction called the BGS-RSCP Auction, while the needs of larger commercial and industrial customers were met through a second and concurrent statewide auction called the BGS-CIEP Auction. Each Auction utilizes a descending clock auction format and bids are submitted online. NERA assisted the four EDCs in formulating the design of the auctions and NERA has managed the process each year on their behalf.
After New Jersey implemented retail choice in August 1999, the state adopted a four-year transition period. During the first three years, (i.e., August 1, 1999 through July 31, 2002), the four New Jersey EDCs supplied those customers who did not switch to a competitive retailer through supply arrangements specified in restructuring settlements using pre-established rates or rate-making processes.
For the fourth year of the transition, the EDCs proposed to procure supply for their BGS customers through a statewide auction. The auction was designed to procure supply for BGS customers at a cost consistent with market conditions and would further the transition in New Jersey by providing an opportunity for energy trading and marketing companies to provide BGS supply. The New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (Board) approved the EDCs' proposal. In February 2002, the first BGS Auction was held and over twenty energy trading and marketing companies competed to provide full-requirements service to BGS customers.
In July of each succeeding year, the EDCs have complied with the directives of the Board by filing a proposal to procure supply to meet BGS load. The EDCs each year have proposed a statewide Auction Process. Other parties each year comment on the EDCs' proposal. After conducting hearings and reviewing comments from all interested parties, the Board makes a decision in late Fall. To date, the Board has approved the EDCs' Auction proposals. Bidders are qualified and registered for the Auctions through a two-part application process that starts in mid-December and ends in mid-January. Bidders that have completed the qualification and registration process can bid in the Auctions held in early February. The Auction utilizes a descending clock auction format and bids are submitted online. Once the Auctions have concluded, the Board renders a decision on the Auction results within two business days. If the Board approves the Auction results, winning bidders have three business days to execute the standard statewide BGS Supplier Master Agreement and to post any required security.
A simultaneous, multiple round, descending clock auction format has been used since the inception of the New Jersey BGS Auction.
The Auction is called simultaneous because all tranches for the load required for each of the four EDCs are put on offer through the same auction. A tranche for one EDC represents a given fixed percentage of that EDC's BGS Load. A tranche in the BGS-RSCP Auction is expected to be close to 100 MW of peak demand while a tranche in the BGS-CIEP Auction is expected to be close to 75 MW. All tranches for the BGS-RSCP load of all four EDCs are procured through the BGS-RSCP Auction. All tranches for the BGS-CIEP load of all four EDCs are procured through the BGS-CIEP Auction.
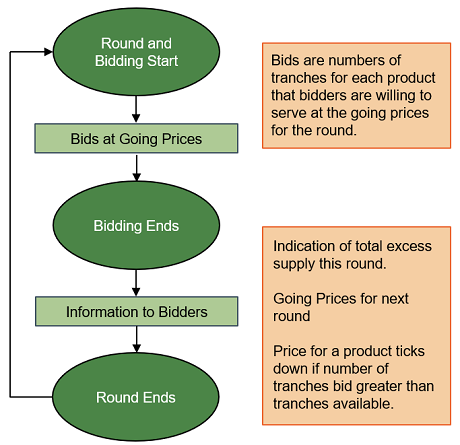
The Auction proceeds in rounds. In a round, the Auction Manager announces a price for each product. A product is either the BGS-CIEP Load or BGS-RSCP Load for an EDC. Bidders bid by providing the number of tranches that they are willing to serve for each product at the prices announced by the Auction Manager. No bidder can bid and win more tranches than the load cap, which is established either on a statewide or on an EDC-specific basis. If the total number of tranches bid is greater than the number of tranches needed for a product, the price for that product is reduced for the next round. Bidders are provided with the next round prices and a measure of excess supply remaining in the Auction. In the next round, bidders are given an opportunity to bid again.
The Auction is called a descending clock auction because prices "tick down" throughout the Auction, starting high and being reduced gradually until the supply bid is just sufficient to meet the load to be procured. Prices that tick down in a round decrease by a decrement; a decrement is a given percentage of the previous price. Bidders holding the final bids when the Auction closes are the winners.
For their BGS-RSCP Load, the EDCs use a rolling procurement structure, where each year one-third of the load is procured for a three-year period. Bidders in a BGS-RSCP Auction bid for the right to serve full-requirements tranches of BGS-RSCP Load for one or more of the EDCs for a term of three years.
The winners of the BGS-RSCP Auction become BGS-RSCP suppliers and are responsible for fulfilling all the requirements of a PJM Load Serving Entity (LSE) including capacity, energy, ancillary services, and any other service as may be required by PJM. Suppliers assume any migration risk and must also satisfy the state's renewable portfolio standards. Suppliers receive an all-in payment based on the auction price for an EDC. The BGS-RSCP customers pay rates derived from the auction clearing prices and these rates vary by season and in some cases by time of day.
Consult each EDC's Company Specific Addendum on the BGS Proceeding page for the details of the rate design methodology. Also see the Additional Data page for each EDC's RSCP Pricing Factors as well as the BGS-RSCP Pricing Spreadsheet, an Excel tool that translates auction prices into rates.
Each EDC's BGS-CIEP Load includes the larger commercial and industrial customers as described in the table below. The supply term is one year, from June 1st to May 31st. Bidders in the BGS-CIEP Auction bid for the right to serve full-requirements tranches of BGS-CIEP Load for one or more of the EDCs for a term of one year.
|

